A small bulge may look harmless at first. Yet, the discomfort slowly turns daily life into a struggle. Laparoscopic hernia surgery gives you a modern and comfortable solution when a hernia interrupts your routine.
Here, you will learn what hernias are, the different types that affect the body, common causes, and the symptoms that require attention. Know which tests are used for confirmation, treatment options, and when to seek timely medical help. This guide helps you understand the condition clearly and choose the right treatment strategy with confidence.
What Is a Hernia?
A hernia develops when tissue pushes through weak muscle walls. It creates a noticeable bulge under the skin or inside the abdomen. Hernias do not shrink or heal without medical support. The bulge often grows over time and becomes painful during movement. Surgery remains the most effective treatment because it restores the muscle structure and prevents the hernia from getting trapped inside.
Common Types of Hernias
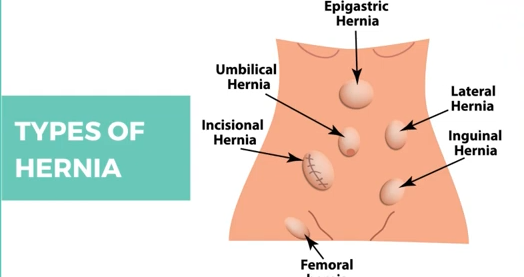
Different types of hernias appear in various body regions. Each type presents unique symptoms and levels of risk.
Inguinal Hernia
This type occurs in the groin area. Men experience it more often because of natural anatomical differences. Pain increases during lifting, coughing, or standing for long hours. The bulge sometimes moves downward into the scrotum. Inguinal hernia treatment usually includes surgical repair.
Umbilical Hernia
This hernia occurs near the belly button when abdominal muscles weaken. It affects both children and adults. The bulge enlarges while coughing, crying, or straining. Umbilical hernia surgery fixes this condition effectively with mesh support for strong results.
Femoral Hernia
Femoral hernias appear low in the groin and occur more often in women. The bulge stays small but carries a higher risk of bowel trapping. Quick treatment prevents complications.
Other Types of Hernia
Hiatal Hernia
This type forms inside the chest. Part of the stomach passes through a diaphragm gap. It causes heartburn, reflux, and breathing trouble. Medical evaluation guides appropriate repair.
Incisional Hernia
This hernia forms at old surgical incisions. Muscle weakness around the scar allows organs to push outward. The risk increases after abdominal surgeries. Strong mesh repair lowers the chance of recurrence.
Spigelian Hernia
This rare hernia appears along the sides of the stomach. The bulge stays hidden under muscle layers. It may go unnoticed until pain increases during movement.
Obturator Hernia
This deep pelvic hernia mostly affects older women. Pain spreads into the upper thigh. Symptoms stay confusing, so the diagnosis sometimes gets delayed. Surgery becomes urgent when the bowel gets trapped.
Diaphragmatic Hernia
Organs push into the chest cavity due to weak diaphragm support. Babies may be born with this defect. Trauma also causes this problem in adults. Early treatment protects breathing and digestion.
Causes and Risk Factors
Weak muscles allow hernias to develop. Several factors increase that weakness over time. These include heavy lifting, obesity, pregnancy, chronic cough, long-term constipation, smoking, ageing, poor muscle tone, and previous surgeries. Genetics and lifestyle habits also contribute to the risk. Preventive steps help lower the chances greatly.
Recognising the Symptoms
Understanding symptoms ensures faster diagnosis. A visible bulge remains the most common sign. The bulge grows during standing, lifting, bending, or coughing. Pain, heaviness, nausea, burning sensations, and digestive trouble also appear, depending on the location. Severe pain or vomiting signals trapped tissue and requires urgent hospital care. Never ignore sudden worsening symptoms.
Diagnostic Approaches
Hernia symptoms and diagnosis are straightforward with a physical examination. Doctors ask you to cough or stand so the bulge becomes more visible. Ultrasound is useful for small or hidden hernias. CT and MRI scans confirm deeper hernias like femoral or obturator types. Proper diagnosis helps choose the safest treatment approach for each patient.
Treatment Options
Hernias require treatment before complications form. The best option depends on the type and severity,
Conservative Management
Support belts offer temporary relief. They do not fix the hernia. Conservative care only applies to very small hernias with zero symptoms. Regular monitoring still remains important.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery repairs the muscle opening and prevents further bulging. Mesh support reduces recurrence and strengthens the area.
Open Surgery
Open repair uses a larger incision over the bulge. Surgeons push organs back and close the muscle gap. This method suits very large or emergency hernias.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic repair uses tiny keyhole incisions. A camera guides the surgeon to fix the hernia internally. Recovery stays quick because of less tissue damage. There is minimal pain, a short hospital stay, and a fast return to life. Laparoscopic hernia surgery is a preferred option for most patients today because it balances safety and comfort.
Postoperative Care
Post-hernia surgery recovery is usually smooth with modern techniques. Patients walk within hours and resume work within days. Follow-up visits ensure proper healing. Doctors share guidelines about activity, diet, and wound care. They also monitor for rare issues like hernia mesh complications.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention matters even after successful repair. Healthy habits keep muscles strong. Focus on maintaining ideal body weight, eating fibre to avoid constipation, lifting objects with correct posture, avoiding smoking, and improving core strength gradually. These hernia prevention tips help protect long-term results.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact the surgeon if the bulge grows, becomes painful, or remains visible even when lying down. Sudden sharp pain with vomiting or no bowel movement signals emergency hernia care. The trapped bowel loses its blood supply, which can lead to life-threatening complications. Immediate help ensures safety and better outcomes.
Navigating Hernia Treatment Options
Hernias start small but worsen over time. Delay increases pain and risk. Safe and effective treatment options exist today thanks to technology and surgical advancements. A skilled hernia specialist in Kolkata helps you understand the condition well and offers the best solution. Laparoscopic hernia surgery in Kolkata ensures quick recovery, minimal pain, and strong long-term repair. The right guidance improves confidence and overall health outcomes.
Expert Hernia Repair with Swasthya Sathi Support
Dr Ashutosh Nayak specialises in modern hernia repair techniques, including laparoscopic surgery. He ensures patient comfort, safer results, and faster healing. He offers Swasthya Sathi services so patients receive advanced hernia care without financial stress. Book your consultation today and regain a pain-free, active lifestyle with expert care in laparoscopic hernia surgery in Kolkata.
People Also Ask
Q1: Can a hernia heal without surgery?
No. Surgery remains the only permanent fix for hernias.
Q2: How do doctors diagnose hernias?
Physical exams and imaging tests confirm the condition.
Q3: Is laparoscopic hernia repair safe?
Yes. It offers quick healing and reduced pain.
Q4: What symptoms indicate an emergency?
Severe pain, vomiting, or a firm bulge needing urgent care.
Q5: Can lifestyle changes prevent hernias?
Healthy weight and proper lifting help prevent muscle strain.
Q6: How long does laparoscopic hernia surgery take?
Most laparoscopic hernia repairs take 45 to 90 minutes.
Q7: When can you return to work after hernia surgery?
Light desk jobs resume within a week. Heavy work needs a doctor’s approval.
Q8: Do all hernias need mesh repair?
Mesh offers stronger results in most cases, but the surgeon decides based on size and location.
Q9: Can hernias come back after surgery?
Recurrence may happen, but modern techniques reduce risks.
Q10: Can you exercise after hernia surgery?
Yes. Start with walking and follow a guided fitness plan after review.